Index Implementation
Adapted from https://builtin.com/data-science/B Tree-index
B Tree
- A balanced tree data structure for maintaining sorted data
- Nodes contain keys and data (or references to data)
- Child pointers in nodes are positioned between keys
Why is it necessary
- Facilitates CRUD operations in logarithmic time due to balanced structure
B+ Tree
- Similar to B Tree but stores data only in leaf nodes
- Internal nodes store keys for navigation
- Leaf nodes are linked together, containing all data
How is it used
| Name | Mark | Age |
|---|---|---|
| June | 5 | 28 |
| Alex | 32 | 45 |
| Tom | 37 | 23 |
| Ron | 87 | 13 |
| Mark | 20 | 48 |
| Bob | 89 | 32 |
Storing table
- Uses B+ Tree for primary key indexing
- Rows are serialized and stored in B+ Tree leaf nodes
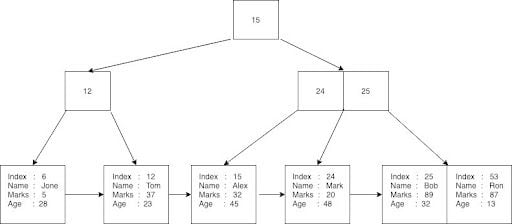
Iterating through table
- Uses binary search and sequential access in B+ Tree
Using the index
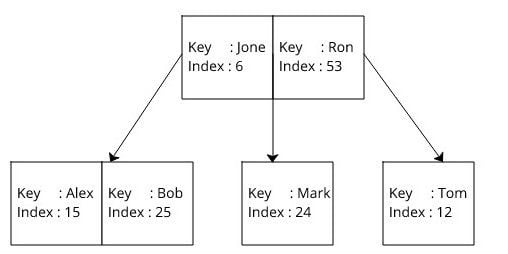
| DS | Use Case |
|---|---|
| B Tree | Often used for indexes where quick search, insertion, and deletion are needed |
| B+ Tree | Preferred for indexing large data sets, particularly for range queries |
Comparisons
| B Tree | B+ Tree | |
|---|---|---|
| Node utilization / Disk I/O Efficiency | Each node holds keys and data (or pointers to data) => limits number of keys each node can hold => deeper tree / more disk reads | Internal nodes only store keys => shallower tree => fewer disk reads |
| Range Queries / Sequential Access | Range queries might require traversal back up anddown to the tree => less efficient | Leaf nodes linked => more efficient range queries / sequential access |
| Key Duplication | No duplicate keys between internal node (key / associated data only stored once) | Keys stored in both leaf / internal nodes |
Conslusion
Efficiency in Different Scenarios: While both B Trees and B+ Trees are efficient, B+ Trees are generally preferred in disk-based systems because they provide better disk I/O efficiency and are more effective for range queries and sequential access
Logarithmic Time Complexity: Both structures indeed offer logarithmic time complexity for basic operations, but the constants involved (like the number of disk reads) can be significantly different, affecting real-world performance
Space Efficiency: If B Trees are only storing pointers (not the actual data), the difference in space efficiency becomes less pronounced. However, B+ Trees still often have an edge due to their structure allowing for more keys per node and thus a shallower tree
